
Thanks to Juan Carlos Iragorri for giving me a couple of minutes to talk about what’s happening with coca cultivation in Colombia on the “Y Esto No Es Todo” podcast produced by Georgetown University’s Americas Institute. (Audio in Spanish)
 “About” pages, including e-mail list signup.
“About” pages, including e-mail list signup.
 Search the site—it’s slow, but it works.
Search the site—it’s slow, but it works.
 Read posts by category (the post’s type or format), by tag (the topic), or by the month I posted it. And link to the RSS feed.
Read posts by category (the post’s type or format), by tag (the topic), or by the month I posted it. And link to the RSS feed.

Thanks to Juan Carlos Iragorri for giving me a couple of minutes to talk about what’s happening with coca cultivation in Colombia on the “Y Esto No Es Todo” podcast produced by Georgetown University’s Americas Institute. (Audio in Spanish)
According to the Colombian daily El Espectador, the UN Office on Drugs and Crime detected 230,000 hectares of coca in Colombia in 2022. That amount—which extends the dark blue line in the chart below to 2022—would be the most coca that the UN agency has detected in any year since it began issuing estimates in 1999.

Colombia was governed for just over the first seven months of 2022 by Iván Duque, and for the remaining less than five months by Gustavo Petro.
Petro was still putting together his government by the time 2022 ended. His drug policy team only published their counter-drug strategy this past weekend. While that is a notably slow pace, it was not the cause for 2022’s result.
Petro has sought to de-emphasize forced eradication of small-scale coca farmers’ crops, which places the government in an adversarial relationship with poor people in historically abandoned territories. Through July, forced eradication is down 79 percent over the same period in 2022. Instead, the new strategy document promotes interdiction, targeting cocaine production and related finances, and other strategies.
Still, critics of the Petro government’s choices will use the 230,000 figure to oppose them. It’s possible, though, that the 2023 coca acreage figure could be reduced, because a historic drop in prices may be making the crop less attractive to many growers.
My thanks to Gonzalo Abarca and Voice of America’s Foro Interamericano program for inviting me to participate as a panelist on September 1. We talked about the status of counter-narcotics efforts in light of my recent mini-report on the collapse of coca markets in Colombia.

Here’s an analysis I’ve been working on, bit by bit, for the past several weeks.
The market in Colombia for coca, the plant whose leaves can be used to produce cocaine, is in a state of historic collapse, bringing with it an acute humanitarian crisis in already impoverished rural territories. The unusually sharp and prolonged drop in coca prices has several causes. WOLA has identified 12 possible explanations, some more compelling than others.
Regardless of the reason, the crisis is sure to be temporary as world cocaine demand remains robust. The Colombian government, and partner and donor governments including the United States, should take maximum advantage of this window of opportunity before it closes. The humanitarian crisis offers a chance for Colombia to fill vacuums of civilian government presence in territories where insecurity, armed groups, and now hunger are all too common.
Read on—in English or Spanish, HTML or PDF—at WOLA’s website.
Colombia didn’t eradicate any coca in January. The police chief cited lack of manpower owing to “contractual and administrative processes.”

(The charts here, showing “0” for January, are from Colombia’s Defense Ministry.)
This translated fragment of a January 31 column in the Colombian daily El Espectador, from María Alejandra Vélez of the University of the Andes’ Center for Security and Drugs Studies (CESED), is a succinct, accurate 2-minute overview of where coca eradication policy stands in Colombia right now, six months into Gustavo Petro’s administration.
Consistent with his campaign discourse, his first announcements, which lack details, aim at not persecuting growers, which includes lowering the tempo of forced eradication and considering a territorial transformation program, which includes gradual substitution once other economies generate income that allows a dignified life for coca growers. He reserved eradication for 20,000 hectares of “industrial” growers, who, as in any market, have already vertically integrated into the market: they cultivate in large tracts, process and market. It remains to be seen if we can identify who they are and where they are.
To stop persecuting small coca growers, 52.7% of whose households live in multidimensional poverty, according to the baseline of households that enrolled in the PNIS, seems obvious to me. Waiting for voluntary eradication to happen when they are already producing and generating income in other economies, too.
Now, the devil is in the details and these are what we should be concerned to know. For example, is there enough funding to attend to the territorial transformation of 200,000 or more families? Will there be a census and registration of small growers according to the size and number of plots? What happens with growers who have several plots? Where will the interventions be focused? For what period of time will the households that stop growing coca be accompanied? How will they be protected from the violence to which armed groups and criminal organizations subject them? How are they going to regain the trust of leaders and their communities to become involved in the policy after decades of non-compliance? What are the plans to prevent the expansion of crops and, in particular, their expansion in environmentally important areas? What types of economies other than coca are viable in ethnic and environmentally strategic territories? How does this whole narrative tie in with Total Peace? Do we have the international leadership necessary to stop chasing coca and talk about a regulatory path for cocaine? How will we measure the success of the new drug policy? Will we be able to convince the Biden administration and other U.S. institutions of the need to focus on solving rural development problems instead of eradication?
That last question is critical for our work here in Washington. Will the Biden administration go along with a counter-drug strategy that relies far less on forced eradication of small farmers’ coca plants?
My sense is that yes, they might. But only if they can be reassured that the Petro government is following a detailed, funded, well-thought-out plan. One that can answer many of the questions in Vélez’s final paragraph here.
Unfortunately, as she notes, the Petro government’s plans so far “lack details.” And that could start complicating the bilateral relationship.
It has long been taken for granted that nearly all coca—the illicit bush whose leaves can be used to make cocaine—is grown in three Andean countries: Bolivia, Colombia, and Peru. If coca bushes pop up elsewhere, local security forces tend to eradicate them quickly.
That may be becoming less true. If you search Twitter for “coca @Ejercito_GT,” you can find a surprising number of official tweets about Guatemalan security-force personnel eradicating coca bushes.
In the past two weeks alone, tweets from Guatemala’s army and government show soldiers and police eradicating coca bushes in four of the country’s twenty-two departments. In some cases, the plants are quite tall, indicating that they’ve been thriving for a while.




This isn’t a consequence of coca becoming scarcer in the Andes and forcing new growing locations. U.S. government estimates indicate that the leaf has never been more plentiful in Bolivia, Colombia, and Peru. It may be a consequence of farmers in Guatemala’s neglected countryside searching for an income-generating crop during a COVID-battered economic moment. It may also be a result of traffickers seeking to do a bit of “nearshoring,” trying to produce cocaine closer to U.S. markets without having to ship it over oceans or through the Central American isthmus.
If it catches on, Guatemala could join the three Andean countries as one of the world’s main coca and cocaine producers, not just a transit country. The elements for coca to catch on are all in place. Proximity to a big market. Vast ungoverned rural spaces with smallholding farmers on the edge of hunger. Widespread, chronic state corruption being abetted by the current government and judicial system. A robust existing network of traffickers who are already doing great damage to fragile ecosystems.
Keep an eye on this.
In this tweet, Honduras’s armed forces report “identifying and securing” a coca field in the country’s rural far east. These bushes are quite tall: they were planted some time ago. Certainly before the term of President Xiomara Castro began nine months ago in late January.
Colombian President Iván Duque spoke twice yesterday at events relevant to U.S.-Colombian relations. At both, he referred to aerial eradication of coca with the herbicide glyphosate, a program that the United States supported between the early 1990s and 2015, when Duque’s predecessor, Juan Manuel Santos, suspended the program out of concern for public health.
I say Duque “referred to” fumigation, because he managed to talk about it without using the words “aerial,” “spray,” “herbicide,” or “glyphosate,” much less “fumigation.” Instead, he used oblique references:
At a seminar about “urban terrorism” organized in Bogotá by the U.S. National Defense University’s Perry Center:
With regard to drug trafficking, we have to continue reducing the area planted with illicit crops, and we have to do it by combining all the tools.
One, manual eradication, for which our country reached the highest figure last year.
Two, alternative development and substitution, but also appealing to the precision mechanisms required in the complex areas of our territory.
At the swearing-in of Colombia’s next ambassador to the United States, former ambassador and former defense minister Juan Carlos Pinzón:
We all know that after you left the Ministry of Defense around 2014-2015 one of the effective methods of fighting illicit crops was suspended. We then saw an exponential jump.
From the beginning of Plan Colombia, when we had 188,000 hectares, until 2014, when we were below 50,000 hectares of coca, the world could see the comprehensive combination of policies. Unfortunately, when that comprehensiveness was fractured and one of the most effective mechanisms was rejected, we saw an exponential jump.
Weird that Duque not only uses such indirect language, but also doesn’t say “we’re going to restart the spray program.” Perhaps drug-policy expert Daniel Rico, who favors fumigation, was correct when he told El Tiempo’s María Isabel Rueda that Duque, with just over a year left in his presidency, has run out of time:
The political, budgetary and technical fight was lost. The President did not realize that within the government itself they were carrying out a turtle operation [deliberate slowdown], and that was what ended the opportunity he had to incorporate aerial spraying.
Q: Who was carrying out the turtle operation?
The National Health Institute, mainly; that is why there will be no aerial spraying in this government. Not as a consequence of a legal problem, because there was always a legal green light to spray, but because there was no leadership to articulate different positions, budgets and interests.
The President was very poorly surrounded on this issue; on the one hand, there was the inexperience of his vice-ministers and, on the other hand, there were obstacles to its implementation.
(Cross-posted from colombiapeace.org)
Colombia’s government is moving closer to reinstating a program, suspended in 2015, that would spray herbicides from aircraft over territories where coca is cultivated. Twenty-five U.S. and Colombian organizations have joined on this letter to President Joe Biden urging him to avoid supporting a renewed “fumigation” program, succinctly laying out the reasons why this would be an unfortunate policy mistake. The letter was shared with the White House on March 26.

March 26, 2021
President Joseph R. Biden, Jr.
The White House
Washington, DC
Dear President Biden,
We write out of strong concern about the imminent restart of a program that your administration is inheriting from its predecessor: an effort to eradicate coca in Colombia by spraying herbicides from aircraft. We encourage you not to provide funding for this program, which not only failed to achieve past objectives, but sends a message of cruelty and callousness with which the United States should no longer be associated. It will undermine the peace accords that are a powerful legacy of the Obama-Biden administration.
Aerial fumigation can bring short-term reductions in the number of acres planted with coca. But past experience shows not only that these gains reverse quickly, but that the strategy undermines other U.S. and Colombian security objectives. Recurring to fumigation is like going back in time, ignoring much that we have learned about what does and does not work.
Many of our organizations have published studies documenting the harm that fumigation has done in the past. The December 2020 report of the U.S. government’s bipartisan Western Hemisphere Drug Policy Commission found that forced eradication brought “enormous costs and dismal results.” Just since the end of February, we have seen strong critiques of forced eradication and fumigation from the International Crisis Group; the Ideas for Peace Foundation, a Colombian business sector think tank; a list of over 200 scholars, and seven UN human rights rapporteurs.
Between 1994 and 2015, a U.S.-backed program supported a fleet of aircraft, and teams of contract pilots and maintenance personnel, that sprayed the herbicide glyphosate over 4.42 million acres of Colombian territory—a land area 3 1/2 times the size of Delaware. In 2015 the Colombian government suspended the spray program, citing public health concerns based on a World Health Organization study finding glyphosate to be “probably carcinogenic to humans.”
For a few years afterward, the Colombian government failed to replace the strategy with anything—neither eradication nor assistance to affected areas. During the late 2010s, Colombia’s coca crop increased to record levels. Nearly all of the increase happened in the exact municipalities and communities where fumigation had been heaviest. After 20 years of constant eradication, farmers continue to face the same on-the-ground reality.
Most Colombian producers of the coca bush are not organized crime-tied criminals or supporters of illegal armed groups. They are families with small plots of land. Estimates of the number of families who make a living off of coca vary from “more than 119,500” to 215,000. If one assumes four people per family, then more than 2 percent of Colombia’s 50 million people depend on coca. Households earn about $1,000 per person per year from the crop, making them by far the lowest-paid link in the cocaine supply chain.
They live in “agricultural frontier” zones where evidence of Colombia’s government is scarce. Paved or maintained roads are nonexistent. The national electric grid is far off. There is no such thing as potable water or land titles. In some areas, even currency is hard to obtain, and stores offer the option of paying for groceries with coca paste.
These people need to be governed and protected by their state. An aircraft flying anonymously overhead, spraying chemicals on populated areas, is the exact opposite of that. But the program has other important disadvantages:
In March 2020, Donald Trump met with Colombian President Iván Duque and told him, “You’re going to have to spray.” The country’s highest court has required Duque’s government to meet a series of health, environment, consultation, and other requirements. Colombia’s Defense Minister is now predicting that the spraying could restart in April.
This time, U.S. Ambassador Philip Goldberg has stated, the U.S. role in the program won’t be as extensive. Still, during the Trump administration, the State Department supported maintenance of the spray plane fleet, upgrades to bases, and training of eradication personnel, among other services. State Department reports sent to Congress in late February and early March hailed fumigation’s imminent restart as a sign of progress.
Nonetheless, we reiterate our hope that the Biden administration will turn away from supporting Colombia’s spray program while there is still time. The United States should not support aerial fumigation in Colombia again. Nor does it have to. We know what to do.
Farmers with land titles hardly ever grow coca. Farmers who live near paved roads hardly ever grow coca. Criminal groups are badly weakened by proximity of a functioning government that is able to resolve disputes and punish lawbreaking.
This is a longer-term project, but Colombia’s 2016 peace accord offered a good blueprint for setting it in motion: a fast-moving, consultative crop substitution program, tied to a slower-moving but comprehensive rural reform program. Though those programs exist and parts of the Duque government are carrying them out diligently, they are underfunded and well behind where they should be as accord implementation enters its fifth year.
It’s not too late to help Colombia jumpstart the model offered by Colombia’s peace accord, which the Obama-Biden administration so effectively supported. We urge you to take that path instead of that of renewed fumigation, which we know to be a dead end.
Sincerely,

Here is the English text of a column that ran today (March 10) in Colombia’s El Espectador.
by Adam Isacson, Director for Defense Oversight, Washington Office on Latin America
“Why is Biden supporting fumigation? I’m so disappointed.” I heard this several times last week from friends in Colombia in the human rights, drug policy, and center-left political opposition communities. It seems they were expecting the new U.S. government to usher in a new era of drug policy in Colombia, and reality hit them in the face.
Their disappointment came mainly from two documents from the U.S. State Department.
The U.S. Congress requires the Department to certify that Colombia is following a strategy to eradicate 50 percent of its coca crop by 2023. It produced that document on February 23, with language celebrating that Iván Duque’s government has made “Significant progress…to re-establish a safe, limited, and targeted Colombian-led aerial eradication program” and that the late Minister of Defense “stated seven AT-802 spray planes were operationally ready to conduct aerial eradication.”
On March 2, the Department produced its annual International Narcotics Control Strategy Report. That document laments that “the Colombian government suspended aerial eradication of coca in 2015, removing a critical tool for reducing coca cultivation,” and celebrates that “President Duque has stated publicly his intent to incorporate aerial eradication into an integrated drug control strategy.”
To many Colombians who have lived through 35 years of forced eradication with poor results, this language looks like doubling down on failure. It may even be viewed as endorsing the Duque government’s view that Colombia’s chronic violence is a result not of unpunished corruption and rural areas’ abandonment, but of the persistence of a bush.
I asked my Colombian colleagues when they ever heard a Biden official say, on the record, that they oppose forced coca eradication. Yes, some people close to Joe Biden were members of the bipartisan commission whose very good December report cites “enormous costs and dismal results” from forced eradication. But then-Senator Joe Biden supported eradication in 2000, when the Congress was considering Plan Colombia, both in a Senate floor speech and a report.
There’s no reason for shock, then, at the past two week’s reports. Still, I don’t advise pessimism. Perspectives change. Plan Colombia began 20 years ago, and the results against coca and cocaine are hardly encouraging.
There’s still ample room for hope that the Biden administration can bring about a historic change in the U.S. approach to coca. Rather than expanding forced eradication, many in the new President’s circle prefer to talk about state presence in territory, provision of services, implementing the peace accord, titling farmers’ land, and building roads. They want to work with a Colombian government that has the will to do the hard work of integrating the countryside into national life. (Whether the current Colombian government has that will is immaterial: it will only be in power for 17 more months.)
A new U.S. approach doesn’t happen with Inauguration Day. There is lag time: U.S. policies don’t change quickly, especially when the presidential transition is as chaotic as ours was. It’s been nearly seven weeks and many key U.S. officials haven’t been named yet. Who will be the new White House Drug Czar? Who will run counter-narcotics at the State Department? Who will run Western Hemisphere Affairs? Who will manage counter-narcotics at the Defense Department? We don’t know yet: this will take months more.
Because the new government is just starting, those two recent reports were “zombie” documents, written by Trump holdovers or career officials. We probably won’t see much change in May, when the Biden Administration, still building its staff, sends to Congress its request for 2022 foreign assistance.
By the second half of 2021, though, things need to start happening. Here is what I’d like to see.
By then, most political nominees to key positions should be in place. Many, if not most, should be reform-minded, not just caretakers.
I would really like to see a fundamental review of drug supply policy happen in late 2021 and early 2022, just as the Biden Administration puts together its foreign assistance request to Congress for 2023. By then, Colombia should be seeing the virus subside and preparing for the campaign for Duque’s successor.
2022 could be a very interesting year. Colombia will have a new government—perhaps one that doesn’t subscribe to the “fumigation will solve violence” view. The Biden government will be consolidated. The Democratic-majority Congress, with old-fashioned hardliners marginalized—will consider what might be a very different 2023 assistance request. There should be opportunities to dialogue with cautious moderates, and to dialogue with Colombian civil society. That’s a prominent request coming from several colleagues and I who accompany AMUNAFRO, la Asociación Nacional de Alcaldes de Municipios con Población Afrodescendientes: “un dialogo serio y profundo, que tenga a las comunidades afectadas como protagonista central,” porque “NO consideramos acertado insistir en lo mismo.”
I could be wrong—but I am optimistic. I’ve got my eye on that period between mid-2021 and late 2022. So I say to my friends in Colombia, don’t despair of the Biden government yet.
Many thanks to our longtime friends and colleagues at the International Crisis group for joining us at this event. Though the topic is complex and often frustrating to teach, everybody explained well what they’ve been learning in the field, and the points that they wanted to get across. The moderation, interpretation, and technical aspects were all spot-on. We had well over 150 live viewers—I was glad to see the number not dropping as we passed the one-hour mark—and at least 200 more since then.
And don’t miss the February 26 ICG report on coca in Colombia, “Deeply Rooted,” on which this discussion centers.
That was a great discussion yesterday. As you could see if you “attended,” our partners in Colombia are very concerned about what might happen if the U.S-funded program of aerial glyphosate fumigation returns to Colombia’s coca-growing zones, as the Bogotá government is promising may happen in two months or less.
I’m pleased that several dozen people tuned in to the live event. Here is the video. There’s no translation track, so you have to be comfortable with Spanish.
We’ll keep making noise about this, because it’s bad policy, it’s going to harm people, and even if it temporarily brings the “hectare” number down, it will do so at great cost to social peace and to Colombia’s peace process.

Colombia has broken its annual record for forced manual coca eradication, and renewed aerial herbicide fumigation looms in 2021.
We’ll be discussing this with some longtime colleagues in Colombia a week from Wednesday: December 9, at 1:30 Eastern. Here’s the text of the event announcement, where you can RSVP. Please share.
(And also — on Friday December 11 I’m putting together a new discussion of COVID-era civil-military relations, covering six countries. Mark your calendar and join for both events if you’re able.)
Four years after the signing of a historic peace accord, hundreds of thousands of Colombian families continue to rely on the coca crop. The government, with U.S. support, has already broken its annual record for forced eradication, during the pandemic, and little of it has been coordinated with food security or rural development assistance. Now, a revival of a controversial aerial herbicide fumigation program is looming.
How are coca cultivating communities responding? How does all of this relate to the peace accord? What might happen if fumigation restarts? What are the costs of eradication, both financially and in terms of rights? Will pursuing the same strategies pursued during the past 30 years really yield a different result? What happened with the peace accords’ crop substitution program? What would a better coca policy look like? How should the new U.S. administration adjust its assistance programs?
WOLA, Elementa, CODHES, the Instituto Pensar of the Universidad Javeriana, the Alianza de Mujeres Tejedoras de Vida, and the Corporación Viso Mutop look forward to addressing these topics on Wednesday, December 9, from 1:30 p.m. to 3:00 p.m. (U.S. eastern and Bogotá time).
Event Details:
Wednesday, December 9
1:30 p.m. – 3:00 p.m. EST
Featuring:
Moderator:
Simultaneous interpretation will be available.
Over the next few weeks I expect to use this space to think some things through in a series of bite-sized but connected posts. I’m going to start with the reality of forced coca eradication and the Colombian government’s larger plan for the millions who live in rural zones where illicit crops and armed groups predominate.
One such zone especially got me thinking: the Guayabero River region in Meta and Guaviare departments, in south-central Colombia about 200 miles south, and 20 hours’ drive, from Bogotá. (I’ve been near here—but not quite this far south—when working on this 2009 report.) In early June and again in early August, this zone saw strong confrontations between coca-growing farmers and security forces.
The main military unit operating in the Guayabero is the Omega Joint Task Force, which has received heavy U.S. assistance since its founding in 2003. Its current commander (who has threatened legal action against local human rights groups) holds degrees from both the National Defense University in Washington and the Army War College in Carlisle, Pennsylvania (which means he probably speaks English better than I do). Omega is one of four units specified to be receiving assistance from a four-month, fifty-three-person detachment of U.S. military trainers that arrived in Colombia at the beginning of June.
The Omega Task Force isn’t accused of killing anyone in these confrontations, but local campesino groups and national human rights groups have leveled some very troubling allegations of rough and aggressive treatment of farmers at the soldiers’ hands. I’ll summarize those in another post.
Omega in the Guayabero is just one example among many of a more combative approach to forced coca eradication this year, and especially since the pandemic lockdown began in March. I discussed this trend in a post in early July, but it’s time to dig deeper.
Here are the points I want to explore over the next few weeks. The outline may change as research accumulates and thoughts evolve.
There have been many more denunciations of aggressive behavior in 2020 than in 2018 or 2019. While coca farmers aren’t models of nonviolence either, the security forces have the guns and the option whether to escalate or de-escalate. Where armed groups are forcing some coca farmers to protest against their better judgment, that should be another reason to de-escalate.
Too much is being guided right now by a single, short-term number: hectares of coca planted in Colombia. The U.S. government is pushing Colombia to cut that number by half in 2023, and Bogotá is pursuing some record eradication targets in order to get there. The number of eradication teams has grown sixfold, much of it with U.S. funding.
Joint Task Force Omega in the Guayabero is a key example. The U.S. Security Force Assistance Brigade that arrived in June is also accompanying military units in two other major coca-growing zones, Catatumbo and Nariño, as well as the nationwide mobile Army Counternarcotics Brigade created with funds from the original 2000 “Plan Colombia” aid package. As eradication operations grow more aggressive, U.S.-aided units’ behavior requires especially tight scrutiny.
Colombia’s defense minister has acknowledged this, as have officials with whom I’ve recently spoken. Leaving coca farming families hungry is not only cruel, it would seem to be a recipe for rapid re-planting. Perhaps it makes sense if the goal is to meet an eradication goal just for 2020, future be damned. But it makes no sense if the goal is to achieve permanent reductions in planting, or to integrate these abandoned territories into the rest of the country.
With no land titling, no government presence, no access to credit, and no farm-to-market roads, coca—an easily transportable product that for years has sold at a reliably steady price—is farmers’ best, and often only, option. Armed groups in some cases require farmers to plant it, and there’s no government nearby to prevent that. Armed groups in some cases are forcing farmers to protest eradication. Campesino leaders, especially those leading coca substitution projects, are being killed in shocking numbers.
Depite all this, when eradicators show up in a territory, who bears the brunt of the security forces’ aggressive behavior? The farmers.
Examples in the past 10 years include the National Territorial Consolidation Program, the Land Restitution Law of 2011, and the 2016 peace accords’ rural reform and crop substitution chapters. None of these efforts is thriving right now.
This is where I’d like to conclude this series of posts. Colombia’s elite seems to show two very different faces to communities in rural areas, including coca cultivators. The same probably applies to the urban poor.
The first face—that of “consolidation,” “stabilization,” land restitution, and the peace accords’ commitments—says to communities, “you can stay where you live.” Even if they don’t see the rural smallholder model as the most efficient approach, they’re willing to direct resources, and in some cases to foster participation.
The second face—that of paramilitarism, “mega-projects,” impunity for social leader killings, refusal to govern territory, and nakedly favoring large landholders—says to communities, “we don’t want you here.” (Or perhaps, “the free market doesn’t want you here”—a message as old as the British Enclosure Movement of the 1700s, and nothing unfamiliar to residents of declining factory towns and poor urban neighborhoods in the United States today.)
Forced, aggressive coca eradication without any food or economic aid? That’s solidly an example of that second face.
The U.S. government supports both faces of Colombia’s elite, to an extent that approaches split-personality disorder. Its aid programs have helped dozens of rural communities to remain where they are and to obtain land ownership, and some military aid programs helped improve Colombia’s overall human rights record. But it also supports aggressive forced eradication and (as we saw in documents released this week) has been too slow or quiet in its response to paramilitarism, social leader killings, and serious human rights abuses.
I’ll be digging more into these questions over the next several weeks.
Every couple of weeks, we get another alert that someone has been killed in Colombia by security forces carrying out coca eradication operations. Those operations are happening under U.S. pressure to go faster, and with lots of U.S. funding, even in the pandemic. And they’re getting more aggressive and violent.
Last Friday, someone else was killed in Putumayo. That appears to be the sixth civilian death since the COVID-19 lockdown began. So I wrote and distributed this commentary on WOLA’s Colombia Peace site.
That dramatic expansion is being helped along by a quarter of a billion dollars in 2020 U.S. assistance for drug interdiction and eradication: $125 million in this year’s foreign aid appropriation, and another $124 million that the Trump administration slashed from aid originally appropriated for Central America, and delivered to Colombia last October. The strategy is being reinforced by a large deployment of military trainers who arrived in the country in early June.
While we don’t have visibility over what is happening inside the Colombian security forces’ eradication teams, it is quite possible that their increased aggressiveness this year is tied to their rapid, U.S.-backed expansion. It’s difficult for any organization to expand this quickly without experiencing managerial issues or slippages in training—including use-of-force training.

Everybody we know is home and on the internet, being “socially distant” for the good of society. Why not start recording conversations with them?
I usually put WOLA’s podcast out 1-2 times per month because my schedule is full and so are those of anyone I’d want to interview. I often spend as much time on the e-mail back-and-forth arranging the episodes as I do recording them.
Not so now. I recorded two today, and have two more scheduled just this week. Here’s the first one:
WOLA Senior Fellow Coletta Youngers and Senior Program Associate Teresa García Castro discuss their February 28 report about women coca and poppy growers in Bolivia and Colombia. It was published with three other organizations from around the region: the International Drug Policy Consortium, Dejusticia, and the Andean Information Network.
The roles played by women in coca and opium poppy producing zones get little attention: they’re often portrayed as passive victims. As Youngers and García Castro explain, women who grow these crops are in fact subjects who lead community organizing, fight for access to land titles, carry out much unpaid labor, and must contend with violence. Development won’t happen without them as partners.
Listen up top, download the mp3 here, and subscribe to the WOLA Podcast wherever you find your podcasts.

(Cross-posted at colombiapeace.org)
We’ve just added a page with nine visualizations of data regarding peace, security, and human rights in Colombia. We’ll update these, and add more, as we make them.
At the bottom of each are shortened links to the documents from which we drew the information. The current collection of infographics covers the demobilized FARC population, U.S. aid, registered victims, U.S. cocaine prices, coca cultivation and eradication, cocaine seizures, homicides, kidnappings, and forced displacement.
We hope you find these useful. Like everything produced by WOLA on this site, you’re free to use them with proper attribution, under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Sometime this year, Colombia is likely to reverse 5 years of policy progress and restore a program that sprays herbicides, from aircraft, over many of the more than 119,500 rural households that live in areas so neglected and abandoned that people grow coca to earn a modest living.
This makes me sad and angry, because Colombia’s 2016 peace accord held so much promise of bringing government, for the the first time, into these forgotten territories that I’ve visited—and been moved by—on many visits to the country. Instead of governing, Iván Duque’s government will be sending contract pilots and police helicopter escorts to fly overhead, spraying the highly questioned chemical glyphosate, with the U.S. government footing much of the bill.
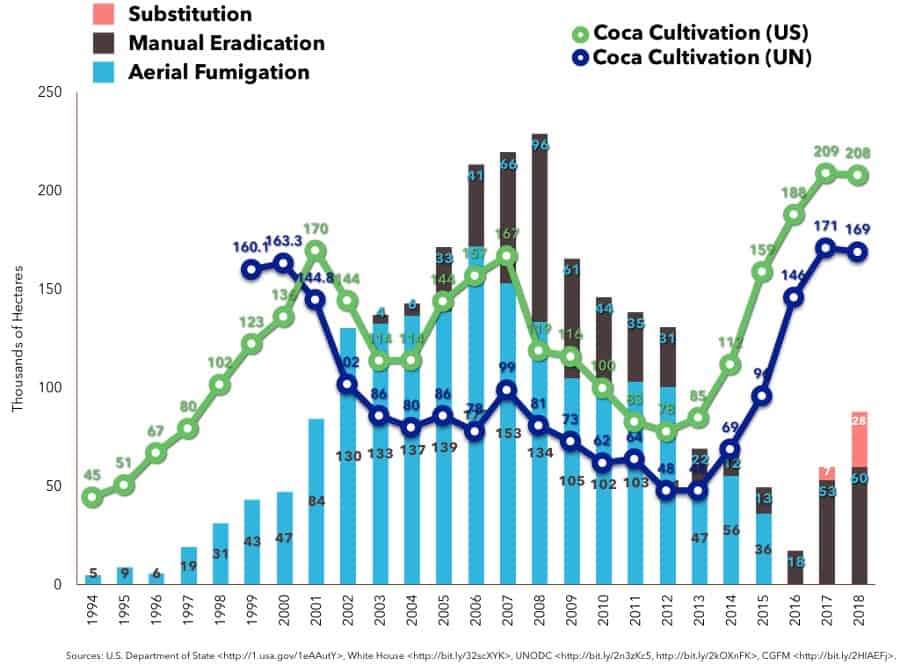
Here’s my latest writing about this, based on a contribution I added to documents submitted by Colombian organizations seeking to challenge the policy in the country’s judicial system. It points out that fumigation may bring short-term reductions in coca growing, but does nothing in the long term but bring high costs, environmental and health risks, a high likelihood of social unrest, and danger to the pilots and other personnel.
I wish they wouldn’t do this: there’s no substitute for governing your own territory and serving your own people.
Read “The Costs of Restarting Aerial Coca Spraying in Colombia” at WOLA’s website.
![A National Police OV-10 plane sprays herbicides over a coca field in Colombia. [AP/WWP file photo]](https://i0.wp.com/2001-2009.state.gov/cms_images/050812_spraying_coca_600.jpg?resize=720%2C512&ssl=1)
On December 30 Colombia’s Ministry of Justice issued a draft decree that would allow it to re-start a U.S.-backed program of aerial herbicide fumigation in coca-growing zones. This program used aircraft to spray more than 4.4 million acres of Colombian territory between 1994 and 2015.
In 2015, a UN World Health Organization literature review found that glyphosate, the herbicide used in the program, was “probably carcinogenic to humans.” In 2018 and 2019, two California juries gave large awards to three U.S. plaintiffs who claimed a link between heavy use of glyphosate and cancer, particularly non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The government of Juan Manuel Santos suspended the coca spraying program in late 2015, but took years before replacing it with any other effort, like alternative livelihoods or manual eradication. As a result of this and other factors, coca cultivation increased dramatically in Colombia. By 2017, more than 119,500 families were making a living off of the crop.
Now, the government of Iván Duque is bringing fumigation back. The U.S. Department of State quickly put out a brief statement celebrating Colombia’s decision.
The decree is 20 pages long, and lays out some of the review, consultation, and complaint processes that should apply to a renewed fumigation program. We’d been expecting this document since July 18, 2019, when Colombia’s Constitutional Court issued a ruling, modifying a 2017 decision, softening the requirements that the government would have to fulfill in order to start fumigating again.
The draft decree is now undergoing a 30-day citizen comment period. Then, it will go to Colombia’s National Drug Policy Council (Consejo Nacional de Estupefacientes), a grouping of ministers, the police chief, the chief prosecutor, and the inspector-general, which must then vote to re-start the program. That vote probably won’t happen until at least March or April. The Colombian journalism website La Silla Vacía sees the process going on for months more:
Several more steps await: that the final decree be issued; that the Defense Ministry formally present a spray program, adjusting to this decree’s requirements, before the National Drug Policy Council; that this Council approves it; and that the Ministry obtains an environmental license for that program. All of that will take several months, and probably most of the year.
Though it loosened restrictions on a new spray program, the Constitutional Court still requires that:
The draft decree excludes from aerial spraying “natural parks of Colombia, whether national or regional; strategic ecosystems like páramos, wetlands as defined by the Ramsar convention and mangroves; populated centers; settlements of populations; and bodies of water.” According to Colombia’s Semana magazine, “researchers consulted…calculate that 70 percent of illicit crops are located in territories where aerial fumigations aren’t viable” under the decree’s definitions because “they are protected zones, because prior consultation is required, or because they are out of the planes’ reach for logistical reasons.”
As in the past, Colombia’s National Police Anti-Narcotics Directorate, a heavy recipient of U.S. assistance, would manage the new spray program. The draft decree gives crucial oversight and approval responsibilities to three small agencies elsewhere within the Colombian government.
These agencies seem quite small, with sporadically updated websites. In some cases they will have to depend on the National Police for logistical support necessary to perform their oversight work. Their capacity to handle a large docket of complaints and monitoring requests is far from assured.
The decree states that the Anti-Narcotics Police must “announce to local and regional authorities, as well as to the citizenry in general, the initiation of spray activities.” This announcement must explain complaint and evaluation mechanisms, and use local media. After spraying in an area, the Narcotics Police must “guarantee participation spaces with local authorities and with the citizenry in general, in which comments, complaints, and suggestions may be expressed.” Conclusions of these “participation spaces” will be included in the Anti-Narcotics Police’s monthly report to the ANLA.
Semana notes that the Constitutional Court had “immovably” required the Colombian government to build a spraying policy “that complies with what was established by the FARC peace accord,” adding that “the expression ‘peace accord’ isn’t mentioned even once in the decree’s text.” The peace accord (section 4.1.3.2) limits aerial spraying only to cases in which communities have not agreed to crop substitution, and where manual eradication is “not possible.”
In cases where there is no agreement with the communities, the Government will proceed to remove the crops used for illicit purposes, prioritising manual removal where possible, bearing in mind respect for human rights, the environment, health and well-being. If substitution is not possible, the Government does not waive the instruments that it believes to be most effective, including aerial spraying to ensure the eradication of crops used for illicit purposes. The FARC-EP consider that in any case of removal this must be effected manually.

Colombia’s Constitutional Court met today to discuss the government’s plans to reinstate aerial spraying of coca. President Iván Duque was the first to address the high court; he asked the justices to “modulate” their past rulings to allow more spraying.
I just posted an analysis of this to WOLA’s website. It addresses a series of questions: